1. Nursery Selection:
For the seedlings of Cephalotaxus fortunei, the best choice is deep soil with a loose structure, rich in humus, and well-drained. It's also possible to choose a mixed forest of coniferous and broad-leaved trees. The breeding base has already solved technical issues such as breaking seed dormancy, cutting propagation, and rooting of seedlings, and selected high-quality Cephalotaxus saplings.
2. Soil Preparation and Fertilization:
Newly cultivated land is naturally fertile and doesn’t require additional fertilizer. For old land, it should be deeply tilled to 20–25 cm, with beds 15–20 cm high and 1.2 m wide, with no limit on length. Apply an appropriate amount of decomposed organic fertilizer, then use 1.5 kg of phoxim per acre to control underground pests and adjust the soil pH. Two weeks before sowing, disinfect the seedbeds with 0.3% potassium permanganate or formalin solution. Water thoroughly, cover with plastic film, leave for a week, and then sow five days later. Drilling can be done as needed.
3. Seed Germination:
(1) New Germination Sowing Method: Before sowing, soak the seeds in a 1%-2% copper sulfate solution for 5 minutes, rinse with water, and then soak them in a 50-degree alcohol and 40-degree warm water mixture (1:1) for 20–30 minutes. Remove and soak in 0.05% gibberellin for 24 hours to activate hydrolytic enzymes, break seed dormancy, and promote early germination.
(2) Alternating Year Burial and Germination Method: Soak the seeds in warm water (around 45°C) for 3–4 days. When the kernels turn milky white, disinfect with 1%-2% copper sulfate solution, then mix with three times wet sand (60% moisture fine sand). Place in a straw bag or wooden box and store in a dry, well-ventilated underground cellar. Choose a high, well-drained location with a pit depth of about 1.5 m to prevent rodent entry. Monitor temperature regularly. In summer, keep it below 20°C; if too hot, open windows at night or use shade nets. Store seeds in autumn, fully buried in the second year, and collect them in spring of the third year. Dry them in the sun for 2–4 days and sow when 20–30% of the seeds have germinated.
(3) Taxus chinensis seeds grow more slowly (usually taking two years). The harringtonia cutting techniques, including dormancy breaking and rooting, have been successfully addressed, and high-quality saplings have been selected.
(4) Winter Burial and Germination Method: This method is suitable for fresh seeds. In autumn, remove the seed coats, soak, disinfect, and mix with sand (similar to the previous method). About 20–30 days before planting, place the seeds in a shaded, leeward area, spread them out, cover with plastic film to increase temperature, and keep them moist. Once part of the seed coat cracks, they are ready for sowing.
4. Seedling Management:
(1) Seedling Protection: If using flat film for seeding, take samples first. Once the radicle emerges, remove the cover and replace it with arch films. After switching to arching, adjust temperature and humidity. On sunny days, open the double agricultural films on the greenhouse to reduce temperature and improve air circulation. Spray water every 3–4 days to maintain 55–60% humidity in the seedbed. Prevent rodent damage.
When the seedlings have two leaves and one heart, uncover them.
(2) Spacing and Transplanting: For Cephalotaxus cuspidata, the general planting density is about 200 seeds per square meter. If the seedlings are too dense and have 3–4 leaves and one heart, transplant them with spacing of 15 cm and 20 cm.
(3) Weeding and Fertilizing: Perform weeding and cultivation 2–3 times, applying 5–10 kg of urea and 3–5 kg of potassium chloride per mu. Water or flood after application. Foliar spray with 0.25% urea and potassium dihydrogen phosphate is also effective.
(4) Pest Control: Cephalotaxus species are generally resistant to pests. Occasional spider mites or aphids may appear. Use pesticides like dichlorvos or dimethoate for prevention and control.
(5) Two-Year-Old Seedlings: Dilute animal manure 3–5 times or ammonium sulfate 1–2 times, spray onto seedlings, and immediately water them to avoid phytotoxicity. From June to July, apply potassium fertilizer to enhance lignification. Strengthen field management, including weeding and soil loosening.
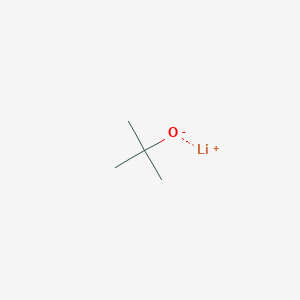
Lithium Tert-butoxide CAS No.1907-33-1
Lithium Tert-butoxide Basic Information
Product Name: Lithium tert-butoxideCAS: 1907-33-1
MF: C4H9LiO
MW: 80.05
EINECS: 217-611-5
Mol File: 1907-33-1.mol
Lithium tert-butoxide Chemical Properties
Boiling point: 68-70 °C
Density: 0.89 g/mL at 20 °C
Fp: −2 °F
Storage temp: Flammables area
Solubility: Soluble in toluene, hexane, tetrahydrofuran and methyl tert-butyl ether.
Form: Liquid
Color: Brown
Specific Gravity: 0.89
Sensitive: Moisture Sensitive
Lithium Tert Butoxide,Lithium Tert-Butoxide,Lithium Aluminum Tert-Butoxide Hydride,Lithium Tert-Butoxide Aluminum Hydride
Shandong YingLang Chemical Co.,Ltd , https://www.sdylhgtrade.com